Difference between revisions of "Event generation"
From Particle Wiki
(Created page with "'''Event generation''' refers to the computer-based simulation of events, usually using the Monte Carlo method and an event generator.") |
(Add event normalisation conventions) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Event generation''' refers to the computer-based simulation of [[Event|events]], usually using the [[Monte Carlo method]] and an [[event generator]]. | '''Event generation''' refers to the computer-based simulation of [[Event|events]], usually using the [[Monte Carlo method]] and an [[event generator]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Choice of event weight normalisation == | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are basically four different choices to normalise event weights ($\langle \cdots \rangle$ denotes the average): | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. <math>\langle w_i \rangle = 1</math> meaning that <math>\langle \sum_i w_i \rangle = N</math> | ||
| + | 2. <math>\langle w_i \rangle = \sigma</math> meaning that <math>\langle \sum_i w_i \rangle = N\sigma</math> | ||
| + | 3. <math>\langle w_i \rangle = 1/N</math> meaning that <math>\langle \sum_i w_i \rangle = 1</math> | ||
| + | 3. <math>\langle w_i \rangle = \sigma/N</math> meaning that <math>\langle \sum_i w_i \rangle = \sigma</math> | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 17 July 2017
Event generation refers to the computer-based simulation of events, usually using the Monte Carlo method and an event generator.
Choice of event weight normalisation
There are basically four different choices to normalise event weights ($\langle \cdots \rangle$ denotes the average):
1. 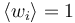 meaning that
meaning that 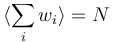 2.
2. 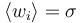 meaning that
meaning that 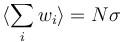 3.
3. 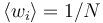 meaning that
meaning that 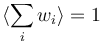 3.
3. 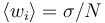 meaning that
meaning that