Difference between revisions of "Sphericity"
(Created page with "The sphericity tensor is the basis for calculation of Event Shape observables, a series of observables particularly suited for <math>e^+ e^- \rightarrow Z^0/\gamma* \rightarro...") |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Physical meaning == | == Physical meaning == | ||
| − | |||
The eigenvector corresponding to <math>\lambda_1</math> is called the sphericity axis. ''S'' measures the amount of <math>p_\perp^2</math> with respect to that axis, and is constrained to values <math>1 \geq S \geq 1</math>. An event with sphericity 0 is a clean dijet event, and sphericity 1 signifies an isotropic event. | The eigenvector corresponding to <math>\lambda_1</math> is called the sphericity axis. ''S'' measures the amount of <math>p_\perp^2</math> with respect to that axis, and is constrained to values <math>1 \geq S \geq 1</math>. An event with sphericity 0 is a clean dijet event, and sphericity 1 signifies an isotropic event. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
| − | == | + | == Data and description == |
Sphericity and aplanarity was measured in all the LEP experiments, and the data are particularly important for tuning of [[parton showers]]. Measurements and comparisons to event generators can be found at MCplots for [http://mcplots.cern.ch/?query=plots,ee,zhad,S sphericity] and [http://mcplots.cern.ch/?query=plots,ee,zhad,A aplanarity]. | Sphericity and aplanarity was measured in all the LEP experiments, and the data are particularly important for tuning of [[parton showers]]. Measurements and comparisons to event generators can be found at MCplots for [http://mcplots.cern.ch/?query=plots,ee,zhad,S sphericity] and [http://mcplots.cern.ch/?query=plots,ee,zhad,A aplanarity]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <math>p_\perp</math> out of the sphericity plane is a particularly interesting observable, as it has been problematic to describe for all the standard parton shower generators, see ''e.g.'' the measurement by [[ALEPH]]: | ||
| + | [[File:http://mcplots.cern.ch/cache/plots/zhad-pToutSph-General-Purpose_MCs.Defaults-aleph1-charged-ee-91-.png|thumb|left|alt=The ALEPH measurement of out of plane transverse momentum.| ss]] | ||
| + | <image></image> | ||
Revision as of 21:36, 24 November 2016
The sphericity tensor is the basis for calculation of Event Shape observables, a series of observables particularly suited for 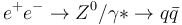 , and routinely used in several LEP analyses.
, and routinely used in several LEP analyses.
Definition
The sphericity tensor is defined as:
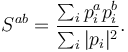
Here 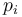 are the four-momenta of all particles in an event. Superscript a and b indicates spatial components, and the sphericity tensor can thus be represented as a 3-by-3 matrix. As such, three eigenvalues can be found. If they are ordered as
are the four-momenta of all particles in an event. Superscript a and b indicates spatial components, and the sphericity tensor can thus be represented as a 3-by-3 matrix. As such, three eigenvalues can be found. If they are ordered as 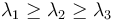 , the sphericity is defined as:
, the sphericity is defined as:
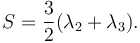
The similar quantity aplanarity is defined as:
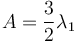
Physical meaning
The eigenvector corresponding to 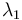 is called the sphericity axis. S measures the amount of
is called the sphericity axis. S measures the amount of 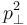 with respect to that axis, and is constrained to values
with respect to that axis, and is constrained to values 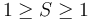 . An event with sphericity 0 is a clean dijet event, and sphericity 1 signifies an isotropic event.
. An event with sphericity 0 is a clean dijet event, and sphericity 1 signifies an isotropic event.
The eigenvectors corresponding to 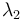 and
and 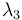 spans a plane, the so-called sphericity plane. Aplanarity measures the
spans a plane, the so-called sphericity plane. Aplanarity measures the 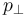 out of that plane, is constrained to
out of that plane, is constrained to 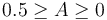 . Similarly to S, A is used to signify the isotropicity of the event.
. Similarly to S, A is used to signify the isotropicity of the event.
Data and description
Sphericity and aplanarity was measured in all the LEP experiments, and the data are particularly important for tuning of parton showers. Measurements and comparisons to event generators can be found at MCplots for sphericity and aplanarity.
The 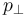 out of the sphericity plane is a particularly interesting observable, as it has been problematic to describe for all the standard parton shower generators, see e.g. the measurement by ALEPH:
out of the sphericity plane is a particularly interesting observable, as it has been problematic to describe for all the standard parton shower generators, see e.g. the measurement by ALEPH:
<image></image>