Difference between revisions of "Cross section"
(Add formula symbol and improve math typesetting) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Basic concept]] | [[Category:Basic concept]] | ||
[[Category:Wikipedia]] | [[Category:Wikipedia]] | ||
| − | The '''cross section''' for a given process is a measure for the rate of interactions that originate from the process that can be quoted independently of the experimental set-up of the scattering experiment itself. In a hypothetical experiment in which a flux of particles | + | The '''cross section''' for a given process is a measure for the rate of interactions that originate from the process that can be quoted independently of the experimental set-up of the scattering experiment itself. It is denoted <math>\sigma</math>. In a hypothetical experiment in which a flux of particles <math>F</math> (incident particles per unit area per unit time) scatter at a rate <math>R</math> (scattered particles per unit time), the cross section is <math>\sigma = R/F</math>. |
Cross sections are measured in units of area, where the special unit ''barn'' (b) is used with prefixes. A barn is 10<sup>−28</sup> m<sup>2</sup> (100 fm<sup>2</sup>). Cross sections at the [[LHC]] can range from hundreds of millibarns (the total cross section of proton-proton collisions) down to fb or smaller for rare processes that are still considered to be measurable. | Cross sections are measured in units of area, where the special unit ''barn'' (b) is used with prefixes. A barn is 10<sup>−28</sup> m<sup>2</sup> (100 fm<sup>2</sup>). Cross sections at the [[LHC]] can range from hundreds of millibarns (the total cross section of proton-proton collisions) down to fb or smaller for rare processes that are still considered to be measurable. | ||
| − | In calculations using natural units (with | + | In calculations using [[natural units]] (with <math>\hbar = c = 1</math>), area has dimensions of 1/energy-squared, so units of [[GeV]]<sup>-2</sup> may be used. The conversion is 1 GeV<sup>-2</sup> = 0.389 mb. |
== Learn more == | == Learn more == | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross_section_(physics) Wikipedia article] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross_section_(physics) Wikipedia article] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:24, 7 April 2017
The cross section for a given process is a measure for the rate of interactions that originate from the process that can be quoted independently of the experimental set-up of the scattering experiment itself. It is denoted 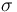 . In a hypothetical experiment in which a flux of particles
. In a hypothetical experiment in which a flux of particles 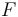 (incident particles per unit area per unit time) scatter at a rate
(incident particles per unit area per unit time) scatter at a rate 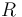 (scattered particles per unit time), the cross section is
(scattered particles per unit time), the cross section is 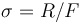 .
.
Cross sections are measured in units of area, where the special unit barn (b) is used with prefixes. A barn is 10−28 m2 (100 fm2). Cross sections at the LHC can range from hundreds of millibarns (the total cross section of proton-proton collisions) down to fb or smaller for rare processes that are still considered to be measurable.
In calculations using natural units (with 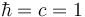 ), area has dimensions of 1/energy-squared, so units of GeV-2 may be used. The conversion is 1 GeV-2 = 0.389 mb.
), area has dimensions of 1/energy-squared, so units of GeV-2 may be used. The conversion is 1 GeV-2 = 0.389 mb.