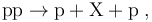Difference between revisions of "Central exclusive production"
From Particle Wiki
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
where <math>\text{X}</math> is any [[system]] in the [[rapidity gap]] between the two [[Final state|final-state]] [[Proton|protons]], hence called ''[[central]]''. The production of <math>\text{X}</math> is ''[[exclusive]]'', because the hadronic final state is fully specified: the scattering protons remain intact and there are no [[beam remnants]] due to breaking-up protons. | where <math>\text{X}</math> is any [[system]] in the [[rapidity gap]] between the two [[Final state|final-state]] [[Proton|protons]], hence called ''[[central]]''. The production of <math>\text{X}</math> is ''[[exclusive]]'', because the hadronic final state is fully specified: the scattering protons remain intact and there are no [[beam remnants]] due to breaking-up protons. | ||
| − | In [[Hadron collision|hadron collisions]] other than proton | + | In [[Hadron collision|hadron collisions]] other than proton-proton, the incoming and outgoing particles are replaced accordingly. |
Revision as of 07:14, 27 April 2016
Central exclusive production is any process of the form
where 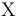 is any system in the rapidity gap between the two final-state protons, hence called central. The production of
is any system in the rapidity gap between the two final-state protons, hence called central. The production of 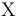 is exclusive, because the hadronic final state is fully specified: the scattering protons remain intact and there are no beam remnants due to breaking-up protons.
is exclusive, because the hadronic final state is fully specified: the scattering protons remain intact and there are no beam remnants due to breaking-up protons.
In hadron collisions other than proton-proton, the incoming and outgoing particles are replaced accordingly.